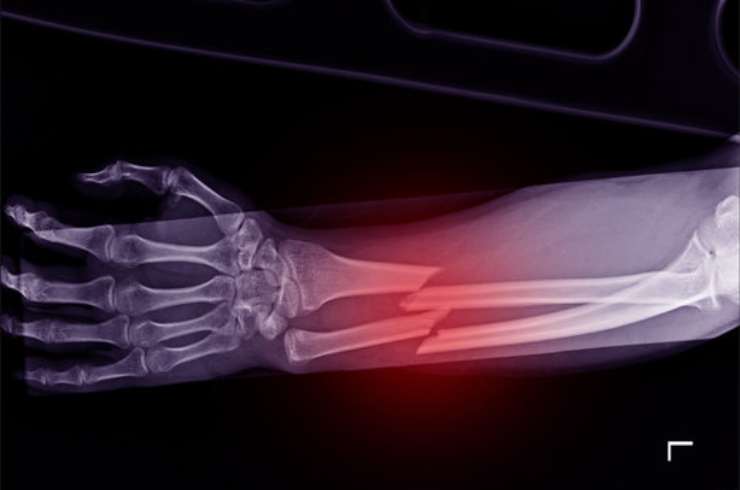
Fracture and trauma surgeries play a vital role in treating injuries resulting from accidents, falls, and other high-impact events. A fracture refers to a break in a bone and may be classified as simple, compound, displaced, or comminuted. Trauma surgeries are designed to manage more complex injuries, including those involving multiple fractures, soft tissue damage, and organ involvement. These injuries often result from road traffic accidents, industrial trauma, or high-energy impacts and require immediate surgical intervention to stabilize the patient and repair structural damage.
Conditions addressed through these procedures include long bone fractures, pelvic and acetabular fractures, spinal injuries, joint dislocations, complex polytrauma, rib fractures, and multiple musculoskeletal injuries. Treatment methods involve reduction (realignment of bones), internal or external fixation using rods, plates, or screws, and in some cases, joint reconstruction or bone grafting. In trauma surgery, emergency procedures may be required to manage internal bleeding and stabilize vital functions. The primary goal is to restore anatomical integrity, support rapid healing, prevent deformity, and promote a return to function. Through advanced surgical techniques and comprehensive post-operative care, these interventions support long-term musculoskeletal health and structural stability.
If you experience intense pain, swelling, visible deformity, inability to move the limb, or if the injury resulted from a high-impact accident, seek immediate medical care. Prompt evaluation helps prevent complications and ensures timely treatment.
Treatment may include immobilization with a cast or splint for simple fractures, while more severe or displaced fractures often require surgical intervention such as internal fixation with rods, plates, or screws.
Recovery depends on the severity of the injury, the surgical procedure performed, and individual healing capacity. Most patients require physical therapy to regain mobility and strength over several weeks to months.
Not all injuries require surgery. Minor fractures may heal with conservative treatment. However, complex fractures or trauma involving multiple injuries may necessitate surgical correction for proper healing.
Follow all post-operative instructions, including activity restrictions, wound care, and physiotherapy. Avoid putting stress on the injured area until cleared by your doctor to ensure proper healing and prevent reinjury.